Post time: Nov-30-2023
The Four Types of Pneumatic Actuators
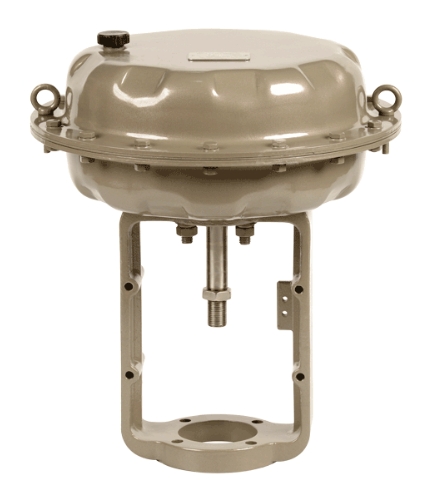
Pneumatic actuators are crucial components in various industrial applications, providing controlled and efficient movement in response to compressed air signals. These actuators come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and operational requirements. In this article, we'll delve into the four main types of pneumatic actuators, exploring their unique characteristics and applications.
1. Pneumatic Cylinders: Linear Motion Powerhouses
a. Basics of Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders, also known as air cylinders, are the most common and straightforward type of pneumatic actuators. They convert compressed air energy into linear motion. The cylinder contains a piston that moves back and forth within the chamber when subjected to compressed air, generating linear force.
b. Single-Acting and Double-Acting Cylinders
Single-Acting Cylinders: These cylinders use compressed air to move the piston in one direction, relying on a spring or other external force for the return movement.
Double-Acting Cylinders: Compressed air powers both the extending and retracting movements of the piston in these cylinders, providing more control over the linear motion.
c. Applications of Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders find widespread use in manufacturing and automation, where linear motion is required for tasks such as lifting, pushing, pulling, and clamping.
2. Pneumatic Rotary Actuators: Turning the Wheels of Industry
a. Basics of Pneumatic Rotary Actuators
Pneumatic rotary actuators convert compressed air energy into rotational motion. They are designed for applications that require turning, oscillating, or rotating movement.
b. Rack and Pinion Mechanism
Many pneumatic rotary actuators use a rack and pinion mechanism, where the compressed air drives a piston connected to a pinion gear, resulting in rotary motion.
c. Applications of Pneumatic Rotary Actuators
Pneumatic rotary actuators are commonly employed in tasks like valve control, conveyor belt positioning, and the operation of rotating machinery.
3. Pneumatic Grippers: Grasping the Possibilities
a. Basics of Pneumatic Grippers
Pneumatic grippers, also known as pneumatic jaws or fingers, are specialized actuators designed for gripping and holding objects. They provide a controlled and adjustable grip using compressed air.
b. Two- and Three-Fingered Grippers
Pneumatic grippers come in various configurations, including two-fingered and three-fingered designs, allowing for flexibility in handling different object shapes and sizes.
c. Applications of Pneumatic Grippers
Pneumatic grippers are widely used in manufacturing processes for tasks such as pick-and-place operations, assembly, and material handling.
4. Pneumatic Bellows Actuators: Flexibility in Motion
a. Basics of Pneumatic Bellows Actuators
Pneumatic bellows actuators utilize a flexible accordion-like structure, known as a bellows, to generate motion. When subjected to compressed air, the bellows expands and contracts, producing linear or angular motion.
b. Applications of Pneumatic Bellows Actuators
Pneumatic bellows actuators are suitable for applications that require precise and controlled expansion and contraction, such as in medical devices, optics, and laboratory equipment.
Choosing the Right Pneumatic Actuator for Your Application
1. Considerations for Selection
When selecting a pneumatic actuator, factors such as the required type of motion (linear or rotary), the degree of precision needed, and the specific tasks the actuator will perform should be considered.
2. Customization Options
Many pneumatic actuator suppliers offer customization options, allowing users to tailor the actuators to their specific application requirements.
Conclusion: Navigating Pneumatic Actuator Variety
In conclusion, the world of pneumatic actuators offers a diverse range of options to suit various industrial needs. Pneumatic cylinders, rotary actuators, grippers, and bellows actuators each bring unique characteristics and capabilities to the table. Understanding the distinctions between these types empowers engineers and manufacturers to make informed choices based on their specific requirements.
For further information on pneumatic actuators or to explore our range of automation solutions, please don't hesitate to contact us.