Post time: Jul-10-2023
Types of Electric Actuators (Rotary, Linear, Multi-turn, Quarter-turn, etc.)
Electric actuators are versatile devices that provide precise and reliable control over mechanical motion. They come in various types, including rotary, linear, multi-turn, and quarter-turn actuators, each suited for specific applications. By understanding the different types of electric actuators and their advantages, industries can make informed decisions when it comes to actuator selection and integration into their systems.
Introduction to Electric Actuators
Electric actuators are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. They are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, chemical, and water treatment. Unlike pneumatic or hydraulic actuators, electric actuators eliminate the need for external power sources, such as compressed air or fluid.
Rotary Actuators
Rotary actuators are designed to provide rotational motion around a fixed axis. They are commonly used in applications that require 360-degree rotation or precise angular positioning. These actuators are suitable for controlling valves, dampers, and other rotating mechanisms.
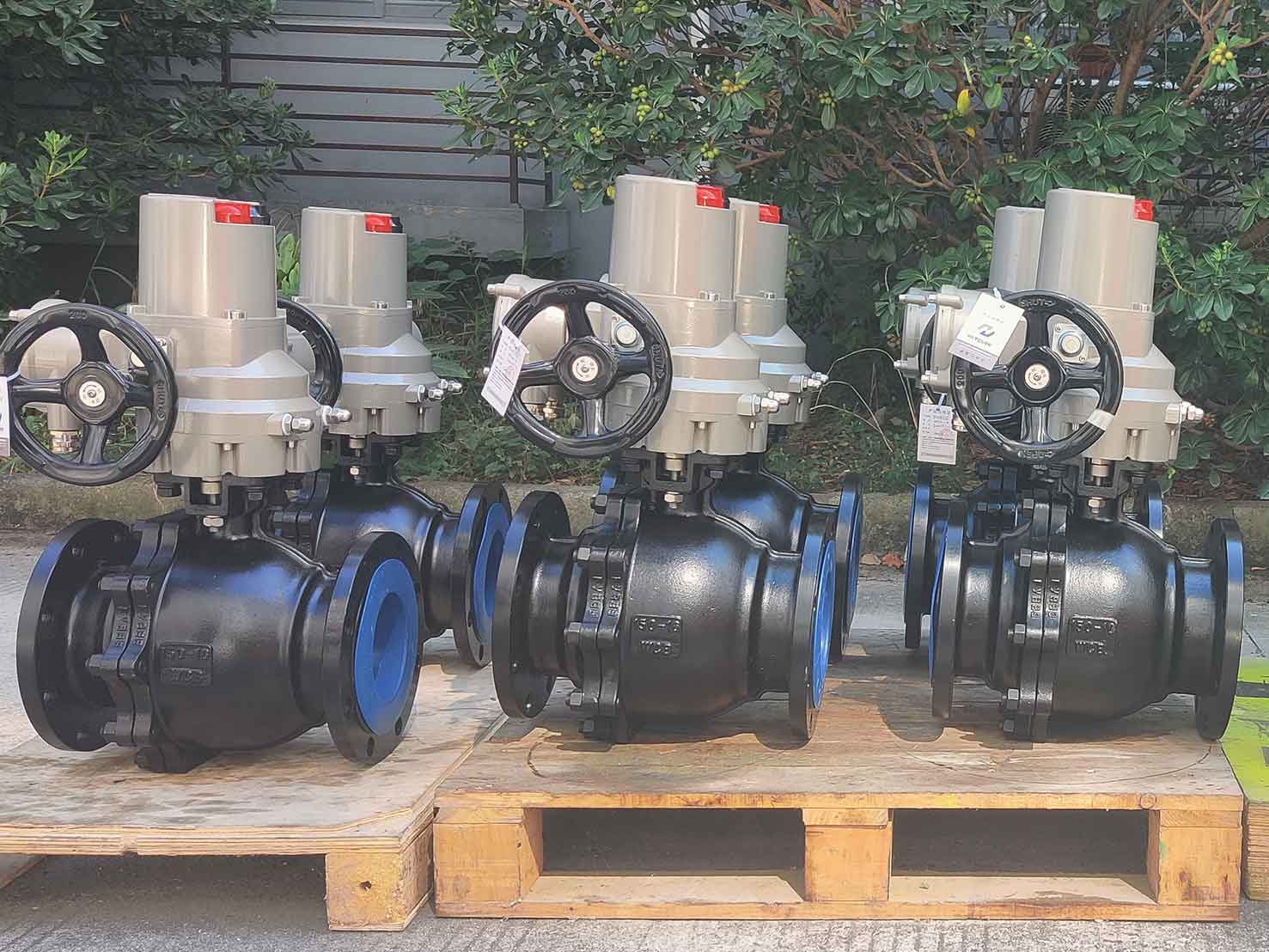

Types of Rotary Actuators
Electric Motor-driven Actuators: These actuators use an electric motor to generate rotational motion. They can be further classified into:
Direct-drive Actuators: These actuators eliminate the need for gears and directly couple the motor to the output shaft. They offer faster response times and higher accuracy.
Stepper Motor Actuators: These actuators use a stepper motor to achieve precise angular positioning. They operate in discrete steps and are commonly used in applications where accuracy is paramount.
Applications
Rotary actuators find applications in various industries, including:
Robotics: Providing rotational motion to robot arms and joints.
HVAC Systems: Controlling air dampers and louvers for efficient airflow management.
Entertainment Industry: Rotating stages, lighting fixtures, and camera platforms.
Advantages
Precise Control: Rotary actuators offer accurate positioning and control over angular motion.Compact Design: They have a compact form factor, making them suitable for space-constrained applications.
Maintenance-free: Electric actuators require minimal maintenance compared to pneumatic or hydraulic actuators.
Automation Capabilities: They can be easily integrated into automated systems, allowing for remote control and monitoring.
Linear Actuators
Linear actuators convert electrical energy into linear motion. They are used to generate push or pull forces along a straight line. Linear actuators find applications in various industries, including automotive, medical, and home automation.
Types of Linear Actuators
Electric Motor-driven Actuators: These actuators use an electric motor to drive a lead screw or a belt mechanism, converting rotary motion into linear motion. They can be further classified into:
Belt-driven Actuators: These actuators use a belt and pulley system to achieve linear motion. They are suitable for applications that require high speed and long strokes.
Solenoid Actuators: These actuators use a solenoid to generate linear motion. They operate by electromagnetism and are commonly used in applications that require quick and short strokes.
Applications
Linear actuators are widely used in the following applications:
Medical Equipment: Adjusting patient beds, controlling surgical tables, and positioning medical devices.
Home Automation: Opening and closing doors, controlling window blinds, and adjusting furniture.
Advantages
Precise Positioning: Linear actuators offer precise control over the position of the actuated mechanism.Compact Size: They have a compact design, allowing for easy integration into space-limited applications.
Energy Efficiency: Electric linear actuators consume less energy compared to hydraulic or pneumatic alternatives.
Smooth Operation: They provide smooth and quiet operation, reducing noise and vibrations.
Multi-turn Actuators
Multi-turn actuators are designed to provide multiple revolutions of rotary motion. They are commonly used in applications that require multiple turns, such as gate valves and multi-turn valves. These actuators ensure precise control over the position of the actuated mechanism.
Types of Multi-turn Actuators
Electric Motor-driven Actuators: These actuators use an electric motor to drive a gear mechanism that enables multiple revolutions. They can be further classified into:
Spur Gear Actuators: These actuators use a series of spur gears to achieve multiple revolutions. They offer higher efficiency and faster response times.
Applications
Multi-turn actuators find applications in the following industries:
Power Generation: Operating turbine bypass valves and other multi-turn valves.
Oil and Gas: Controlling pipeline valves and safety valves in oil and gas facilities.
Advantages
Precise Position Control: Multi-turn actuators allow for accurate positioning over multiple revolutions.Self-locking Capability: Certain types of multi-turn actuators have a self-locking mechanism, eliminating the need for external brakes or locks.
High Torque Output: They provide high torque output, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Maintenance-friendly: Electric multi-turn actuators require minimal maintenance compared to their hydraulic counterparts.
Quarter-turn Actuators
Quarter-turn actuators are designed to providerotational motion of 90 degrees or a quarter of a full revolution. They are commonly used in applications that require quick and precise actuation, such as ball valves and butterfly valves.
Types of Quarter-turn Actuators
Electric Motor-driven Actuators: These actuators use an electric motor to drive a mechanism that achieves a 90-degree rotation. They can be further classified into:
Scotch Yoke Actuators: These actuators use a scotch yoke mechanism to convert rotary motion into linear motion. They offer high torque output and precise control.
Hydraulic or Pneumatic Actuators: Although the focus of this article is on electric actuators, it's worth mentioning that quarter-turn actuators can also be powered by hydraulic or pneumatic systems. These systems use fluid pressure to generate the required actuation force.
Applications
Quarter-turn actuators are widely used in various industries for applications such as:
Oil and Gas: Operating pipeline valves, including ball valves and plug valves.
Chemical Processing: Controlling valves in chemical plants and refineries.
HVAC Systems: Actuating dampers and control valves for efficient airflow management.
Advantages
Fast and Precise Actuation: Quarter-turn actuators provide quick and accurate actuation, ensuring efficient operation.Compact Design: They have a compact form factor, making them suitable for applications with limited space.
High Torque Output: Electric quarter-turn actuators offer high torque output, enabling them to handle demanding loads.
Easy Installation and Integration: Electric actuators can be easily installed and integrated into existing systems, reducing downtime during installation.
Comparison of Electric Actuator Types
When selecting an electric actuator for a specific application, it's essential to consider several factors:
Cost: The cost of electric actuators can vary based on their type and features. Rotary and linear actuators tend to be more affordable compared to multi-turn and quarter-turn actuators, which often require additional mechanisms and components.
Maintenance: Electric actuators, in general, require less maintenance compared to pneumatic or hydraulic actuators. However, the maintenance requirements can vary depending on the specific type and design of the actuator.
Control Options: Electric actuators offer various control options, including manual control, remote control, and automated control through programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or other control systems. The control options should align with the specific requirements of the application.
FAQs
What is the lifespan of an electric actuator?Electric actuators have a long lifespan, typically ranging from 10 to 20 years, depending on the specific application, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions.
Can electric actuators be used in hazardous environments?
Yes, electric actuators can be designed to meet the requirements of hazardous environments, such as those with explosive gases or dust. They can be equipped with appropriate enclosures and certifications to ensure safe operation.
Are electric actuators suitable for high-speed applications?
Yes, electric actuators can achieve high speeds, especially when coupled with direct-drive mechanisms. However, the speed capabilities can vary depending on the specific actuator type and design.
Can electric actuators be retrofitted to existing systems?
Yes, electric actuators can often be retrofitted to existing systems, providing an upgrade from manual or other actuation methods. However, it's essential to consider compatibility, space limitations, and potential modifications required during the retrofitting process.
What factors should be considered when selecting an electric actuator?
When selecting an electric actuator, factors such as the required motion type (rotary or linear), torque or force requirements, control options, environmental conditions, and budget should be taken into account to ensure the actuator meets the specific needs of the application.
For more information see "The Ultimate Guide to Electric/Pneumatic Actuators, Valve Actuators, and Industrial Actuators"